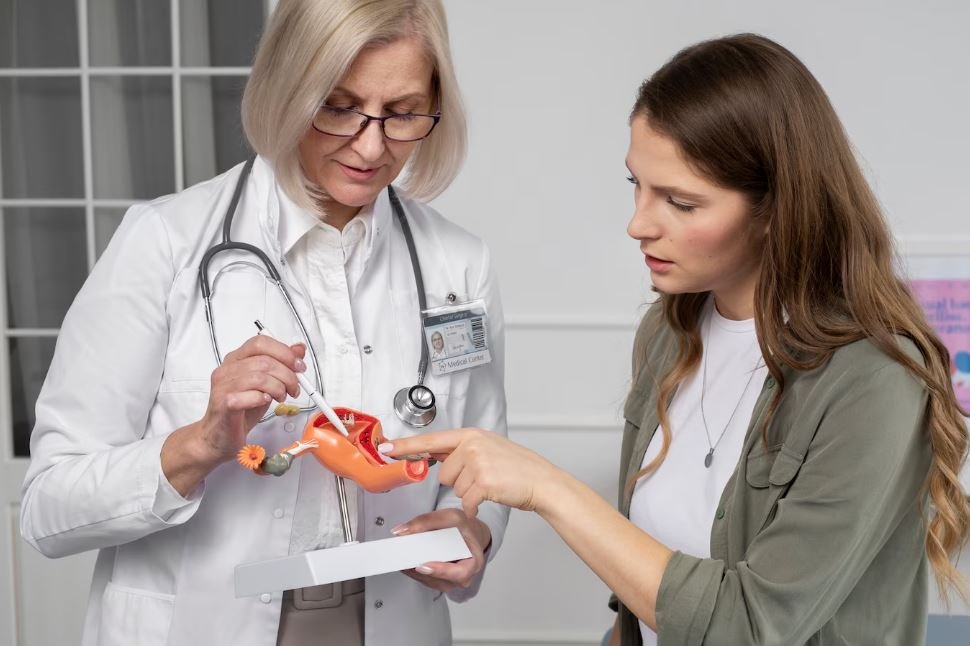
Gallstones, diminutive solidified accumulations of bile that develop in the gallbladder, can induce significant pain and health issues. Although surgery is frequently the preferred solution for numerous cases, a growing contingent of individuals is pursuing nonsurgical alternatives to address the issue. Due to apprehensions regarding surgery or a preference for less invasive alternatives, various options exist for alleviating symptoms associated with gallbladder issues. This article examines the diverse nonsurgical therapies for gallstones and their efficacy.
Gallstones impact millions, with numerous individuals suffering from pain or digestive disturbances. Although cholecystectomy has traditionally been the standard surgical intervention, various nonsurgical methods exist to manage, dissolve, or eliminate gallstones. For individuals seeking to circumvent surgery, these alternatives may offer an efficacious solution, though with differing levels of effectiveness.
Top Nonsurgical Treatments for Gallstone Removal
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
| Oral Dissolution Therapy | Medications like ursodiol dissolve cholesterol-based gallstones, though this may take months to years. |
| Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) | A minimally invasive procedure that removes gallstones from the bile ducts using specialized instruments. |
| Shock Wave Lithotripsy | Focused sound waves break gallstones into smaller pieces that can be naturally expelled. |
| Percutaneous Cholecystostomy | Insertion of a tube to drain the gallbladder, offering a temporary solution for high-risk patients. |
| Endoscopic Gallbladder Stenting | A stent is placed to help bile drainage, especially for patients who are not candidates for surgery. |
| MTBE Injection | A solvent injected into the gallbladder to dissolve stones, though it carries risks and is used sparingly. |
- Oral Dissolution Therapy: Perseverance Yields Results
Oral dissolution therapy represents a conservative method for the treatment of gallstones. Medications such as ursodiol or chenodiol function by reducing the viscosity of bile in the gallbladder, thereby facilitating the dissolution of cholesterol-based calculi over time. This method can be highly effective for specific patients, but it necessitates patience. Treatment may span several months to a few years, and there remains a possibility of gallstone recurrence following the conclusion of therapy. Although it progresses slowly, oral dissolution therapy offers a non-invasive method for managing cholesterol gallstones without surgical intervention, rendering it a significant alternative for numerous patients.
- Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography (ERCP): Specific Calculus Extraction
Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) provides an effective, non-invasive treatment for gallstones situated in the bile ducts. This procedure employs an endoscope, introduced via the oral cavity, to extract stones from the bile ducts. In certain instances, ERCP may be employed to dilate bile ducts or to insert stents to enhance bile flow. ERCP is especially advantageous for individuals facing complications such as cholangitis (bile duct infection) or when surgical intervention is not feasible. It is less invasive than conventional surgery and can be highly effective in alleviating symptoms caused by bile duct stones.
- Shock Wave Lithotripsy: Fragmenting Calculi with Acoustic Waves
Shock wave lithotripsy (SWL) is a technique that employs acoustic waves to disintegrate gallstones into smaller particles, facilitating their natural passage through the digestive tract. This technique is most efficacious for isolated, diminutive calculi and is generally designated for instances where the stones measure less than 2 cm in diameter. SWL is traditionally utilized for kidney stones but is increasingly being applied in the treatment of gallstones. Although it is a non-invasive technique, it is not applicable to all patients, as only a limited percentage qualify for the procedure. Additionally, SWL is typically integrated with oral dissolution therapy to enhance long-term results.
- Percutaneous Cholecystostomy: A Transitory yet Essential Alternative
In specific high-risk patients, where surgery is not immediately feasible due to other health issues, Percutaneous Cholecystostomy (PC) can provide temporary alleviation. This procedure entails the insertion of a catheter through the dermis to evacuate fluid from the gallbladder. This is not a definitive solution, but it aids in symptom management and diminishes the likelihood of infection or inflammation. For patients too unwell to immediately undergo surgery, palliative care offers a crucial intervention until their health sufficiently improves to allow for more definitive treatment options.
- Endoscopic Gallbladder Stenting: Ensuring Patency
Endoscopic gallbladder stenting offers an innovative solution for patients unable to undergo surgery while managing their gallstone issues. This procedure entails the insertion of a stent in the bile ducts, facilitating normal bile flow and averting obstructions due to gallstones. Although stents do not eliminate gallstones, they assist in symptom management by promoting bile drainage from the gallbladder. This is an optimal selection for patients who encounter considerable surgical risks and may not be suitable candidates for more invasive interventions.
- MTBE Injection: A Disputed Yet Efficacious Chemical Remedy
Methyl tertiary-butyl ether (MTBE) is a compound capable of dissolving gallstones by decomposing their structure. It is administered directly into the gallbladder and acts rapidly to dissolve stones. The procedure entails risks, including intense burning pain, and must be conducted in a regulated setting. Due to the potential for severe side effects and the necessity for specialized knowledge, MTBE is typically employed only in rare circumstances. Notwithstanding the possible disadvantages, MTBE continues to be a viable alternative for certain patients who have not benefited from other nonsurgical interventions.
Lifestyle Modifications: Preventing Cholelithiasis Without Surgical Intervention
Nonsurgical treatments effectively manage existing gallstones; however, prevention is the optimal strategy. Embracing a nutritious lifestyle—abundant in fruits, vegetables, and lean proteins—while sustaining a healthy weight can markedly diminish the likelihood of gallstone formation. Eschewing a high-fat diet, ensuring adequate hydration, and participating in consistent physical activity are essential measures for preserving gallbladder health. Furthermore, regulating conditions such as diabetes and obesity via lifestyle modifications can diminish the likelihood of gallstone development.
Exploring Your Gallstone Treatment Alternatives
For individuals with gallstones, surgical intervention is not the sole alternative. Nonsurgical interventions such as oral dissolution therapy, endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP), shock wave lithotripsy, and stenting offer efficacious alternatives for managing the condition without resorting to invasive procedures. Nonetheless, selecting the appropriate method necessitates meticulous evaluation of the size, type, and location of the gallstones, in addition to the patient’s overall health status.
By investigating these nonsurgical options and collaborating with a healthcare professional, patients can identify the most appropriate treatment for their gallstone concerns while circumventing the risks and recuperation period linked to surgery. By employing the appropriate methodology, gallstones can be effectively managed, allowing for the restoration of a healthy, pain-free existence.